このコンテンツは役に立ちましたか?
どうすればこの記事をもっと役立つものにできると思いますか?
Administrator's Guide - Audit Log Management
Audit logs are detailed records of activities in the Lyve Cloud console and S3 API operations. Audit logs are used to access audit functions and track any suspicious activity.
When you enable audit logging, all audit logs are written to the selected target bucket. The target bucket must be immutable, which keeps audit logs immutable. For more information, see Using object immutability. You cannot switch off object immutability for the target bucket. You can maintain three types of audit logs:
- S3 API audit logs: This log records all supported S3 API calls. For more information, see Supported S3 API calls.
S3 API audit logs are recorded in theS3-<BUCKET-NAME>-<TIMESTAMP>.gzformat, where theBUCKET-NAMEis the name of a bucket being logged. For more information, see Example S3 API audit log. - IAM audit logs: This log includes all events corresponding to identity and access management actions.
IAM audit logs are recorded in theIAM-<TIMESTAMP>.gzformat. For more information, see Example of IAM audit log. - Console audit logs: This log includes all the events that originated from the Lyve Cloud console's actions.
The console audit log is recorded in theconsole-<TIMESTAMP>.gzformat. For more information, see Example of the console audit log.
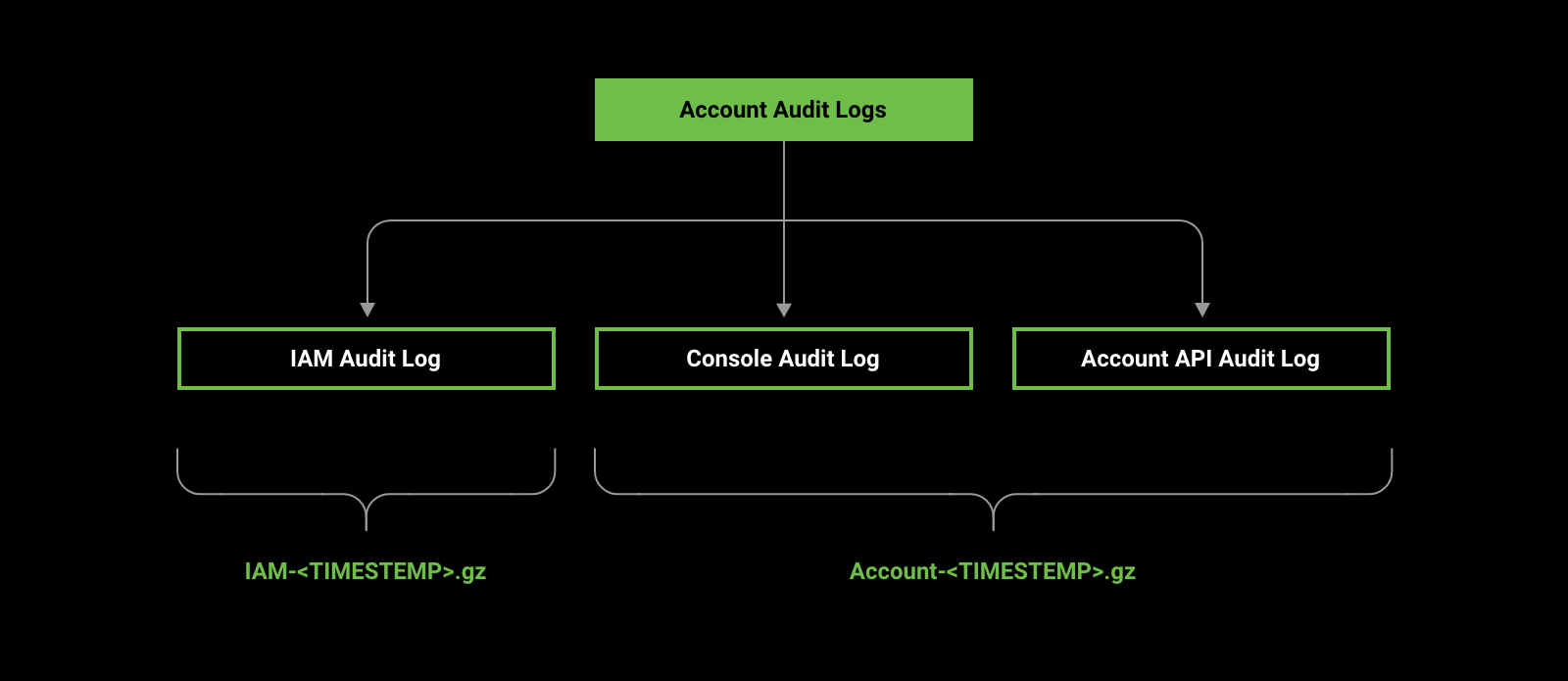
The audit log files have TIMESTAMP format: yyyy-MM-dd-HH-mm-ss' and are set to the UTC zone.
Audit log files keep sufficient information to establish which events occurred, when they occurred, and who caused them. Administrators can manually delete these audit log files after the specified retention duration ends. This helps you to manage the buckets cost-effectively. For more information, see Using object immutability.
Lyve Cloud periodically saves audit logs for specified buckets. The maximum size of a log file is 500 MB. If the file size reaches 500 MB, that log file is saved, and the logs continue to be written in a new file. Log files are saved to the target bucket as console audit log files, IAM audit logs, or S3 API logs.
Role-based access to permission
The following table describes access to enable and disable audit logs based on your role.
| Actions | Admin | Storage Admin | Auditor (Read only) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enable/disable S3 API audit logs | ✓ | × | × |
| Enable/disable account audit logs | ✓ | × | × |
| Edit audit log target bucket | ✓ | × | × |
| View audit log settings | ✓ | × | ✓ |
Video: Lvye Cloud - How to manage audit log settings in the Lyve Cloud console
Seagate on Vimeo: Lyve Cloud - How to manage audit log settings in the Lyve Cloud console
S3 API audit logs
S3 API audit logs keep detailed records of activity in the Lyve Cloud console as well as S3 API operations. To enable S3 API audit logs, you must select buckets to be logged from the target buckets available in the account.
Example S3 API audit log
The following is an example of an S3 API audit log file.
{
"serviceAccountCreatorId":
"john.doe@email.com",
"auditEntry":
{
"api":
{
"name": "PutObject",
"bucket": "bucket-1",
"object": "values-v2.yaml",
"status": "OK",
"statusCode": 200,
"timeToResponse": "2246401314ns" },
"time": "2021-01-22T10:49:30.699378337Z",
"version": "1",
"requestID": "165C883E70C2A5D0",
"userAgent": "aws-sdk-java/1.12.25 Linux/4.15.0-135-generic OpenJDK_64-Bit_Server_VM/11.0.12+7 java/11.0.12 vendor/Oracle_Corporation cfg/retry- mode/legacy",
"remotehost": "127.0.0.1",
"deploymentid": "ef46b1cb-6be1-4aa2-9c14-e7ffbc11986b",
"requestHeader":{
"User-Agent": "aws-sdk-java/1.12.25 Linux/4.15.0-135-generic OpenJDK_64-Bit_Server_VM/11.0.12+7 java/11.0.12 vendor/Oracle_Corporation cfg/retry-mode/legacy",
"X-Amz-Date": "20210122T104928Z",
"Content-Type": "text/yaml",
"Authorization": "AWS4-HMAC-SHA256 Credential=AHPEVYIPHVQ3XNOY/20210122/us-east-1/s3/aws4_request, SignedHeaders=content-type;host;x-amz-content-sha256;x-amz-date, Signature=<redacted>",
"Content-Length": "5637",
"X-Amz-Content-Sha256": "UNSIGNED-PAYLOAD",
"X-Amz-Server-Side-Encryption": "AES256" },
"responseHeader":{
"ETag": "219857b61eb0c3dc9a3916a0992fc803",
"Vary": "Origin",
"Server": "LyveCloud/DEVELOPMENT.2020-06-22T03-43-44Z",
"Accept-Ranges": "bytes",
"Content-Length": "0",
"X-Amz-Request-Id": "165C883E70C2A5D0",
"X-Xss-Protection": "1; mode=block",
"Content-Security-Policy": "block-all-mixed-content",
"X-Amz-Server-Side-Encryption": "AES256"
}
},
"serviceAccountName": "serv-acc-01"
}
The following table describes the parameters specified in the S3 API audit log file.
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
serviceAccountCreatorId |
A user who created the service account. |
name |
Specifies the API name. |
bucket |
Specifies the bucket name. |
object |
Specifies the object name. |
status |
Specifies the HTTP status. |
statusCode |
Specifies the HTTP status code. |
timeToResponse |
Time for the entire request to complete. |
time |
The timestamp in UTC zone. |
version |
Represents the current version of Audit Log structure. |
requestID |
A unique request identifier. |
userAgent |
Specifies the User-Agent request header |
remotehost |
Displays IP address of the client who sent the request |
deploymentid |
A unique deployment identifier. |
requestHeader |
Specifies the request header content. |
responseHeader |
Specifies the response header content. |
serviceAccountName |
Displays the name of Service Account associated with buckets. |
Enabling S3 API audit logs
To enable S3 API audit logs:
- On the left-hand menu, select Settings.
- On the Audit Logs Settings page, set S3 API Audit Logs to ON to begin saving audit logs.
- In the Audit Log Target Bucket dialog, select the target bucket from the list to store the logs.
Set the target bucket only if you are setting the target bucket to write audit logs for the first time. However, if you have already set the target bucket while enabling console audit logs, you are not forced to select the target bucket.

- Select Save.
After you enable the S3 API audit log:
To change the target bucket:
- On the Audit Log Settings page, a new 'Audit Log Target Bucket' section is displayed. This section displays the target bucket name and bucket region. To change the target bucket, see Editing audit log target bucket.
To set the S3 API audit logs:
- Select which buckets will have audit log.
- All buckets must be logged: Selecting this option allows you to set and enforce logging for all available buckets in the account. By default, this option is selected.
- Individually set per bucket: Selecting this option allows you to edit each bucket to enable logging manually.
After selecting the Individually set per bucket option, you must choose each bucket individually and then enable the S3 API audit logs. To enable S3 API audit logs for an individual bucket, see Editing bucket properties. Once S3 audit logs are enabled, the selected bucket in the account is labeled as Logged.

Disabling S3 API audit logs
While enabling S3 API Audit Logs, if you select the Individually set per bucket option and later disable audit logs, the S3 API Audit Logs option will be unavailable in that individual bucket.
To disable S3 API audit logs:
- On the left-hand menu, select Settings.
- On the Audit Log Settings page, set S3 API Audit Logs to Off.
After you switch off S3 API audit logs, the Logged label is removed from all buckets.
Console audit log
Enabling account audit logs enables Console Audit Logs, IAM Audit logs, and Account API Audit logs.

Before you enable them, become familiar with the account audit logs by reviewing the examples below.
Example of Account API audit log structure
{
"ApiEvent":
{
EventName: “<eventname>”,
Version: “2”,
Request: {
AccountName: “service account name”,
AccessKey: “<accesskey>”,
RequestTime: “<hh:mm:ss>”,
RequestParams: {
…. Parameters.. or Body
},
SourceIP: “XXYYXX”
},
Response: {
ResponseTime: “<response time>”,
ResponseCode: “<response code>”,
ResponseError: “<error>”,
ResponseBody: { …
body…. (with secret redacted) …
}
}
| Event name | API action |
|---|---|
authenticate-and-get-session-token |
Authenticate and get a session token |
Test-a-session-token-for-validity |
Test a session token for validity |
get-historical-storage-usage-by-month |
Get historical storage usage by month |
get-current-month-storage-usage |
Get current month storage usage |
list-permissions |
List permissions |
create-a-new-permission |
Create a new permission |
get-permission-by-id |
Get permission by id |
delete-a-permission-by-id |
Delete a permission by id |
update-a-permission |
Update a permission |
list-service-accounts |
List service accounts |
create-a-new-service-account |
Create a new service account |
get-service-account-data-by-id |
Get service account data by id |
delete-a-service-account-by-id |
Delete a service account by id |
update-a-service-account |
Update a service account |
enable-a-service-account |
Enable a service account |
disable-a-service-account |
Disable a service account |
enable-audit-logging-on-a-bucket |
Enable Audit logging on a bucket |
disable-audit-logging-on-a-bucket |
Disable Audit logging on a bucket |
Example of an account audit log
The following is an example of the console audit log file.
{
"ConsoleVersion": "DEVELOPMENT",
"DeploymentID": "dell2",
"LoginTime": "2021-01-25T09:19:11.622206Z",
"UserIdentity": {
"EventSource": "https://dell2.console.localhost:32428",
"UserName": "john.doe@email.com",
"Role": "admin",
"IPAddress": "10.244.142.100:34310"
},
"ConsoleEvent":
{
"Eventname": "add-new-notification-recipient",
"Status": "Error while inserting data to table: ",
"StatusCode": 13,
"EventResponse": "{\"Action\":\"Add NotificationRecipient\",\"FirstName\":\"Fname\",\"LastName\":\"Lname\",\"Email\":\"john.doe@email.com\",\"Partner\":\"dell2\",\"AddedBy\":\"john.doe@email.com\"}",
"EventTime": "2021-01-25 09:37:01.505980988 +0000 UTC m=+1421.228517562"
}
}
The following table includes console operations recorded in the console audit log. The Event name column displays the names inside the console audit log as an eventname parameter value.
| Event name | Console operation |
|---|---|
create-bucket |
Create bucket |
delete-bucket |
Delete bucket |
create-permission |
Create permission |
set-object-immutablility |
Set object immutability |
create-permission-from- imported-file |
Create permission from an imported file |
edit-permission |
Edit permission |
delete-permission |
Delete permission |
create-service-account |
Create service account |
edit-service-account |
Edit service account |
service-account-status-change |
Service account status change |
service-account-deletion |
Delete service account |
add-user |
Add user |
user-password-reset |
User password reset |
edit-user |
Edit user |
user-enabled-disabled |
User enabled/disabled |
user-logout |
User log out |
create-support-ticket |
Create support ticket |
edit-support-ticket |
Edit support ticket |
new-comment |
New comment |
add-new-notification- recipient |
Add new notification recipient |
remove-notification-recipient |
Remove notification recipient |
edit-notification-recipient |
Edit notification recipient |
on-off-s3-api-audit-log |
On/off S3 API audit log |
on-off-s3-console-audit-log |
On/off Console audit log |
s3-api-audit-log-setting |
S3 API audit log setting |
s3-api-audit-log-bucket-setting |
3 API audit log bucket setting |
The following table describes the parameters specified in the console audit log file.
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
consoleVersion |
Displays the console version |
deploymentid |
The unique deployment identifier |
loginTime |
The timestamp in UTC zone |
eventSource |
The console URL path |
userName |
The login ID of the user |
role |
The Lyve Cloud user role |
ipAddress |
The user identity IP address |
eventname |
Specifies the console operation |
status |
Displays the human-readable message |
statusCode |
Displays the status numeric code. For more information, see Status Code table. |
eventResponse |
Displays the resulting action performed by the event name |
eventTime |
Displays the timestamp in UTC zone |
Status code
The following tables provide descriptions for the StatusCode parameter.
| Status code | Error | Error details |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | OK Code | OK is returned on success. |
| 1 | Cancelled Code | The operation is cancelled by the client. |
| 2 | Unknown Code | Specifies an unknown error.For example, errors raised by APIs that do not return enough error information. |
| 3 | InvalidArgument Code | The client specifies an invalid argument. |
| 4 | DeadlineExceeded Code | The operation has expired before completion.This error may be returned even if the operation has completed successfully, however, the response is delayed.For example, a successful response from a server could have been delayed long enough for the deadline to expire. |
| 5 | NotFound Code | Requested entity (file or directory) was not found. |
| 6 | AlreadyExists CodeA | An attempt to create an entity failed because one entity already exists. |
| 7 | PermissionDenied Code | The caller does not have permission to execute the specified operation. |
| 8 | ResourceExhausted Code | Some resource has exhausted. |
| 9 | FailedPrecondition Code | The operation was rejected because the system is not in a state to execute the operation.For example, directory to be deleted may not be empty. |
| 10 | Aborted CodeT | The operation was aborted due to a concurrent issue like sequencer check failures, transaction aborts, etc. |
| 11 | OutOfRange Code | The operation was attempted past the valid range.For example, seeking or reading past end of a file. |
| 12 | Unimplemented Code | The operation is not implemented, supported, orenabled for this service. |
| 13 | Internal Code | Indicates internal errors, where some invariants have broken. |
| 14 | Unavailable Code | The service is currently unavailable. |
| 15 | DataLoss Code | Indicates unrecoverable data loss or corruption. |
| 16 | Unauthenticated Code | The request does not have valid authentication credentials for the operation. |
Example of an IAM audit log
The following is an example of an IAM audit log file.
{
"created_date":"2021-01-20T02:04:12.000Z",
"organization":"random-org",
"org_type":"TENANT",
"source":"console",
"created_by"::"IAM",
"content":{
"date": "2016-02-23T19:57:29.532Z",
"type": "sapi",
"description": "",
"connection": "",
"connection_id": "",
"client_id": "AaiyAPdpYdesoKnqjj8HJqRn4T5titww",
"client_name": "My application Name",
"ip": "190.257.209.19",
"hostname": "190.257.209.19",
"user_id": "auth0|56c75c4e42b6359e98374bc2",
"user_name": "",
"audience": "",
"scope": "",
"strategy": "",
"strategy_type": "",
"log_id": "",
"isMobile": false,
"details": {},
"user_agent": "",
"location_info": {
"country_code": "",
"country_code3": "",
"country_name": "",
"city_name": "",
"latitude": "",
"longitude": "",
"time_zone": "",
"continent_code": ""
}
}
"bucket_name":""
}
The following is an example of an IAM audit log file.
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
created_date |
Date when the event occurred in ISO 8601 format. |
organization |
Name of the account. |
org_type |
Displays the type of organization Partner|Tenant. |
source |
Displays source of the Log. |
created_by |
Displays which service created the log. |
content |
IAM log content. |
bucket_name |
Target bucket name where the log files are stored.Optional and can be left blank. |
The following table describes the data field for contents in the IAM audit log file.
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
date |
Date when the event occurred in ISO 8601 format. |
type |
Type of event. For more information, see Event code list associated with each log event. |
description |
Description of the event. |
connection |
Name of the connection for the event. |
connection_id |
ID of the connection for the event. |
client_id |
ID of the client (application). |
client_name |
Name of the client (application). |
ip |
The IP address of the log event source. |
hostname |
Hostname where the event is applied. |
user_id |
User ID involved in the event. |
user_name |
User name involved in the event. |
audience |
API audience for whom the event is applied. |
scope |
Scope permissions applied to the event. |
strategy |
Name of the strategy involved in the event. |
strategy_type |
Type of strategy involved in the event. |
log_id |
Unique identifier of the event. |
isMobile |
Specifies if the client is a mobile device (true), desktop, laptop, or server (false). |
details |
Additional details about the event (the structure is dependent upon event type). |
user_agent |
User agents details from the client device that caused the event. |
location_info |
Displays information about the location that triggered this event based on the IP. |
The following table describes the data field for location_info.
| Parameter name | Description |
|---|---|
country_code |
Displays the country code in two-letter Alpha-2 ISO 3166-1 format. |
country_code3 |
Displays the country code in a three-letter Alpha-3 ISO 3166-1 format. |
country_name |
Full country name. |
city_name |
Full city name. |
latitude |
Global latitude (horizontal) position. |
longitude |
Global longitude (vertical) position. |
time_zone |
Time zone name. |
continent_cide |
Displays continent of the country.For example, AF (Africa), AN (Antarctica), AS (Asia), EU (Europe), NA (North America), OC (Oceania) or SA (South America). |
The following table describes the event code associated with each log event.
| Event Code | Description |
|---|---|
admin_update_launch |
Update launched. |
api_limit |
The maximum number of requests to theauthentication API in given time has been reached. |
cls |
Passwordless login code/link has been sent. |
coff |
AD/LDAP connector is offline. |
con |
AD/LDAP connector is online and working. |
cs |
Passwordless login code has been sent. |
depnote |
Deprecation notice. |
du |
User has been deleted. |
f |
Failed login. |
fc |
Failed by connector. |
fce |
Failed to change user email. |
fco |
Origin is not in the allowed origins list for the specified application. |
fcoa |
Failed cross-origin authentication. |
fcp |
Failed change password. |
fcph |
Failed post change password hook. |
fcpn |
Failed change phone number. |
fcpr |
Failed change password request. |
fcpro |
ailed to provision a AD/LDAP connector. |
fcu |
Failed to change username. |
fd |
Failed to generate delegation token. |
fdeac |
Failed to activate device. |
fdeaz |
Device authorization request failed. |
fdecc |
User did not confirm device. |
fdu |
Failed user deletion. |
feacft |
Failed to exchange authorization code for access token. |
feccft |
Failed exchange of access token for a client credentials grant. |
fede |
Failed to exchange device code for access token. |
fens |
Failed exchange for native social login. |
feoobft |
Failed exchange of password and OOB challenge for access token. |
feotpft |
Failed exchange of password and OTP challenge for access token. |
fepft |
Failed exchange of password for access token. |
fepotpft |
Failed exchange of passwordless OTP for access token. |
fercft |
Failed exchange of password and MFA recovery code for access token. |
fertft |
Failed exchange of refresh token for access token. |
ferrt |
Failed exchange of rotating refresh token. |
flo |
User logout failed. |
fn |
Failed to send email notification. |
fp |
Failed login (incorrect password). |
fs |
Failed signup. |
fsa |
Failed silent auth. |
fu |
Failed login (invalid email/username). |
fui |
Failed to import users. |
fv |
Failed to send verification email. |
fvr |
Failed to process verification email request. |
gd_auth_failed |
Multi-factor authentication failed. This could happen due to a wrong code entered for SMS/Voice/Email/TOTP factors, or a system failure. |
gd_auth_rejected |
A user rejected a Multi-factor authentication request via push-notification. |
gd_auth_succeed |
Multi-factor authentication success. |
gd_enrollment_complete |
A first time MFA user has successfully enrolled using one of the factors. |
gd_otp_rate_limit_exceed |
A user, during enrollment or authentication, enters an incorrectcode more than the maximum allowed number of times. Ex: A user enrolling in SMS enters the 6-digit code wrong more than 10 times in a row. |
gd_recovery_failed |
A user enters a wrong recovery code when attempting to authenticate. |
gd_recovery_rate_limit_exceed |
A user enters a wrong recovery code too many times. |
gd_recovery_succeed |
A user successfully authenticates with a recovery code. |
gd_send_pn |
Push notification for MFA sent successfully sent. |
gd_send_sms |
SMS for MFA successfully sent. |
gd_send_sms_failure |
Attempt to send SMS for MFA failed. |
gd_send_voice |
Voice call for MFA successfully made. |
gd_send_voice_failure |
Attempt to make Voice call for MFA failed. |
gd_start_auth |
Second factor authentication event started for MFA. |
gd_start_enroll |
Multi-factor authentication enroll has started. |
gd_tenant_update |
Guardian tenant update. |
gd_unenroll |
Device used for second factor authentication has beenunenrolled. |
gd_update_device_account |
Device used for second factor authentication has beenupdated. |
limit_delegation |
Rate limit exceeded to /delegation endpoint. |
limit_mu |
An IP address is blocked with 100 failed loginattempts using different usernames, all with incorrect passwords in 24 hours, or 50 sign-up attempts per minute from the same IP address. |
limit_wc |
An IP address is blocked with 10 failed loginattempts into a single account from the same IP address. |
pwd_leak |
Someone behind the IP address: ip attempted to login with a leaked password. |
s |
Successful sign-on event. |
sapi |
Success API operation. |
sce |
Success change email. |
scoa |
Success cross-origin authentication. |
scp |
Success change password. |
scph |
Success post change password hook. |
scpn |
Success change phone number. |
scpr |
Success change password request. |
scu |
Success change username. |
sd |
Success delegation. |
sdu |
User successfully deleted. |
seacft |
Successful exchange of authorization code for access token. |
seccft |
Successful exchange of access token for a client credentials grant. |
sede |
Successful exchange of device code for access token. |
sens |
Native social login. |
seoobft |
Successful exchange of password and OOB challenge for access token. |
seotpft |
Successful exchange of password and OTP challenge for access token. |
sepft |
Successful exchange of password for access token. |
sercft |
Successful exchange of password and MFA recovery code for access token. |
sertft |
Successful exchange of refresh token for access token. |
srrt |
Successfully revoked a refresh token. |
slo |
User successfully signed out. |
ss |
Success signup. |
ssa |
Silent auth. |
sui |
Successfully imported users. |
sv |
Verification email. |
svr |
Verification email request. |
sys_os_update_end |
Update ended. |
sys_os_update_start |
Update started. |
sys_update_end |
Update ended. |
sys_update_start |
Update started. |
ublkdu |
User block setup by anomaly detection has been released. |
w |
Warnings during login. |
Enable account audit logs
To enable the account audit log:
- On the left-hand menu, select Settings.
- On the Settings page, set Account Audit Logs to ON.
- in the Audit Log Target Bucket dialog, select the target bucket from the list to store the logs.
You must set the target bucket only if you are setting the target bucket to write audit logs for the first time. However, if you have set the target bucket while enabling S3 API audit logs, you are not forced to select the target bucket again.
Only the buckets that are in immutable are displayed in the list. - Select Save.
Disable account audit logs
To disable account audit logs:
- On the left-hand menu, select Settings.
- On the Settings page, set Account Audit Logs to OFF.
After you disable audit logs:
- Logs are no longer saved to the target bucket.
- The target bucket is still visible in the Audit Logs Target Bucket section.
Edit audit log target bucket
While editing the target bucket to save audit logs, only immutable buckets are displayed for selection.
To edit console audit logs:
- On the left-hand menu, select Settings.
- In the Audit Log Target Bucket section, select Edit.

- On the Edit Audit Log Target Bucket dialog, select the target bucket from the Select bucket list and then select Save.